Crypto Transaction Fees: A Simple Overview

Crypto fees are the cost you pay to process transactions on a blockchain network. They’re called different names depending on the blockchain — for example, “gas fees” on Ethereum, “Tx fees” on Bitcoin, and so on. However, the idea is the same — you pay miners or validators who maintain the network to process and approve your transaction. In this short guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about crypto fees.
Types of Fees in Crypto
Network transaction fee (network fee)
The network transaction fee is the main type of fee in crypto that you pay for processing any transaction in the network. It can be a transaction, sending tokens, interacting with dApp, etc.
When you send a transaction, it needs to be included in the blockchain. Blockchain additions are made by validators (in Proof-of-Stake) or miners (in Proof-of-Work). You pay a small network fee to have your transaction included.
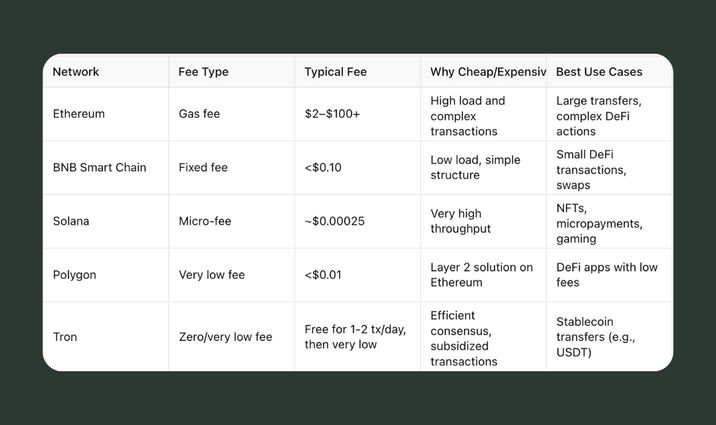
There is an interesting thing in Ethereum. The network transaction fee is called a “gas fee”. Its cost depends on network congestion and the complexity of the operation. Gas prices are expressed in Gwei (where 1 ETH = 1,000,000,000 Gwei).
Exchange fees
When you use centralized exchanges (like Binance, Bybit, or OKX), they charge fees for trading and transactions. A trading fee is applied to every order — whether you’re buying or selling.
There are two types of trading fees: maker fees — when you add a new order (limit order) — and taker fees — when you fill someone else’s order (market order).
There are also fees for deposits and withdrawals:
- These include fees for fiat deposits (via card or bank transfer) and crypto withdrawals.
- The fee amount depends on the network. For example, Binance allows you to choose the withdrawal network — withdrawing via BSC is usually cheaper than via Ethereum.
Wallet fees
Many cryptocurrency wallets, especially those that work with Web3 apps and support token exchange right inside the interface, may also charge fees. These fees are not for storing your funds (wallets are free in that sense) but for using additional features.
Fees in Coin Wallet
Coin Wallet lets you manage many different types of cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana, TRON, and more than 200 coins.
The fees you pay when using Coin Wallet depend on the specific cryptocurrency and the type of transaction. You also pay a service fee that helps cover wallet development, server maintenance, and team support.
Network fees
When sending cryptocurrency through Coin Wallet, users pay network fees. These fees depend on the network's current load and the type of transaction. For example, fees on the Ethereum network are often higher due to the use of smart contracts, while fees on Solana are typically lower.
Buying and selling cryptocurrency
Through Coin Wallet, users can buy and sell cryptocurrencies using various payment methods, including credit/debit cards, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and bank transfers. Fees for these transactions depend on the selected payment method and current market rates.
Security and privacy
Coin Wallet emphasizes the importance of security and privacy. Private keys are stored only on the user’s device, and there is no need to complete KYC (Know Your Customer) verification to use the wallet.
If you have specific questions about fees for a particular cryptocurrency or transaction, please send them to support@coin.space.
Here, we have collected all the key information about fees in Coin Wallet.
Tips for Saving on Crypto Fees
-
Choose the right network when withdrawing from an exchange
For example, do not withdraw USDT via Ethereum if you can use TRC20 — it could save some money. However, you should check the current fee information beforehand. You can do this in Coin Wallet: go to the All About Fees page, then click on the network (Ethereum or TRON). -
Watch the network load
Services like Etherscan's Gas Tracker show current gas fees on Ethereum. If fees are too high, it’s better to wait for a less busy time. -
Use aggregators
When swapping tokens inside a wallet, aggregators like 1inch or Matcha find the best rates and factor in transaction fees. -
Top up your gas token in advance
For example, if you plan to use the Polygon network to send tokens, make sure you have some POL in your wallet to cover gas fees.