Understanding XRP Transaction ID: A Simple Example

XRP is the main rival of SWIFT in the fintech market today. In addition, Ripple has already partnered with Santander, Bank of America, PNC, SBI Holdings, and other major players. In January 2025, Ripple launched its own stablecoin (RLUSD). In this article, we are going to discuss Ripple, its products, and the meaning of ID transactions.
What is XRP?
It all started with the emergence of Ripple in 2012. At that time, it was named OpenCoin, and its main idea was to create a way to make international transactions cheaper and faster than through SWIFT. After many improvements in 2015, Ripple evolved into its current form and offered two types of technologies:
-
XRP is the native cryptocurrency of the Ripple ecosystem. The coin operates exclusively within the Ripple network via the XRP Ledger (XRPL) and is primarily used for fast international transactions. It is also the native token on the XRP Ledger that was created for use in the system. All 100 billion XRP were released all at once, and today, Ripple has the majority of the assets. This fact is often controversial in the crypto community because it raises questions about the network's decentralization.
-
XRP Ledger (XRPL) is a decentralized, distributed, open-source blockchain that serves as the foundation for XRP transactions.
XRP Ledger isn't a traditional blockchain in the technical sense because it doesn't use PoW and PoS. In a traditional blockchain (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum), data is stored in a chain of blocks, with each block containing transaction information. In XRP Ledger, the information is recorded in a ledger, which is updated every 3–5 seconds because it uses the Ripple Protocol Consensus Algorithm (RPCA) that allows transactions to be validated in 3–5 seconds for a minimal fee. In comparison, Bitcoin does it in 10 to 60 minutes (10 minutes per block on average, but confirmation may take longer depending on network load and fees). The average Ethereum transaction time is between 15 seconds and 15 minutes.
That's why XRP Ledger can be seen as an alternative blockchain. It serves the core functions of a blockchain: decentralized data storage, transaction security, and immutability of records.
Additionally, XRPL doesn't have the mining and staking processes typically used for transaction validation. In XRPL, validators confirm transactions through voting, making the validation process faster and more energy-efficient.
Where to find XRP ID transaction?
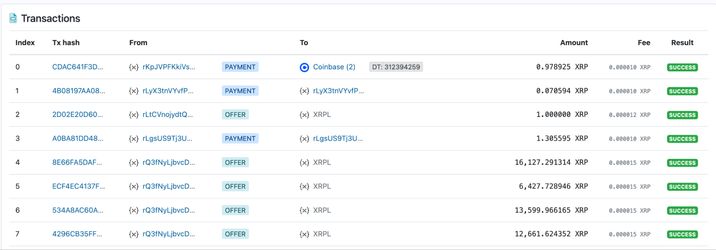
XRP Transaction ID is a unique hash — a string of 64 alphanumeric characters (hex-code) — that is used to identify a specific transaction on the network. Simply put, the XRP Transaction ID is your transaction receipt on the XRP Ledger blockchain.
XRP Transaction ID example:
- 4B08197AA08211396E447A1DE6F7134851AB6B0370BD89C09A0D742446E053B7
- 5AD5704BE4DDF9F93E86EA4CBA57DA292BEEBDE982E7CE9EF89DEEFB9A3ADB1B
This code is recorded on the XRP Ledger and allows you to track the status of the transaction.
To find your transaction ID, you can use a blockchain explorer, such as Blockchair.com or wallets and scanners, like xrpscan.com. In this case, type your XRP address in the search box and press Enter.
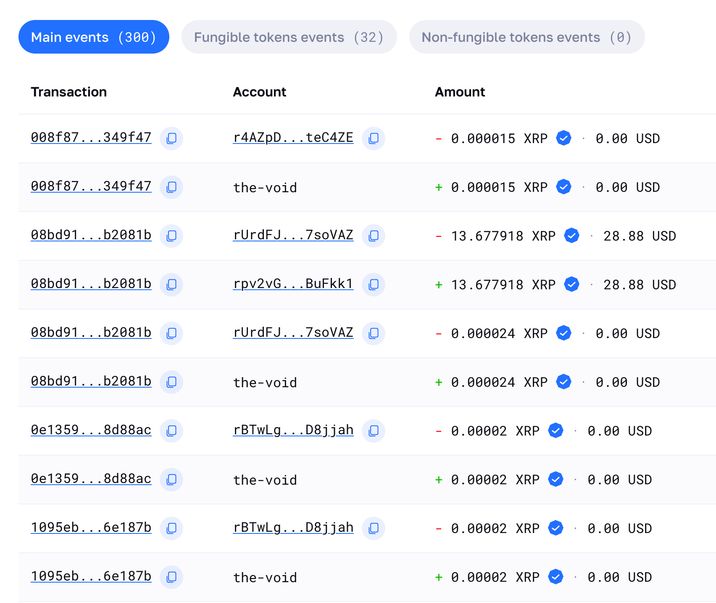
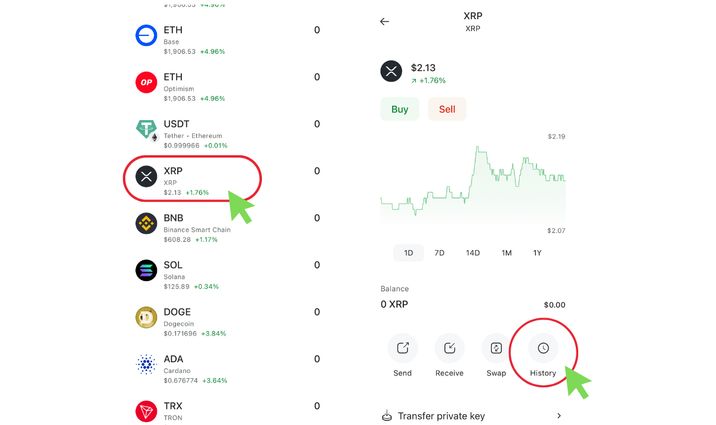
Also, you can use Coin Wallet, of course. Use your unique passphrase to log in to Coin wallet, select the coin, and check the transaction details in the ‘History’ section.