What is AVAX and the Snowman Consensus Protocol

Early May 2025 has seen a significant increase in interest from large AVAX holders. According to IntoTheBlock, net inflows from large investors increased 380% in a week, which could signal a price jump to $30 if the trend continues. If you want to catch a wave and make a well-considered investment, this AVAX review is for you.
Key Takeaways
- Avalanche allows you to create public and private subnets, develop dApps, and do it fast, cheaply, and with a high level of security.
- This blockchain is a major rival to Ethereum.
- Avalanche uses a family of consensus protocols called “Snow”. It includes three consensus mechanisms: Avalanche, Snowman, and Frosty.
- AVAX is the native token of the Avalanche blockchain and is available in Coin Wallet.
What is Avalanche (AVAX)?
Avalanche is a blockchain platform created in 2018 to launch dApps and deploy public and private blockchains in its own ecosystem.
Avalanche includes two levels of the network: the Primary Network and an unlimited number of Subnets. Unlike Ethereum or Bitcoin, where work is being done in one chain, Avalanche separates processes among three chains to avoid overload:
- The Platform Chain (P-Chain) stores metadata and is responsible for coordinating validators and monitoring subnets.
- The Contract Chain (C-Chain) allows users to create Ethereum-compatible smart contracts.
- The Exchange Chain (X-Chain) provides tools for exchanging data between subnets and creating interchangeable tokens and NFTs.
Avalanche subnetworks are similar to L2 solutions for Ethereum and parachains in Polkadot, but with completely isolated blockchain states.
Users can create their own subnets in Avalanche. It is especially useful for businesses. For example, if a company wants to use blockchain technology for storing and transferring sensitive information, it can create its own separate subnet in Avalanche and ensure the data remains private.
Therefore, Avalanche is a blockchain that allows users to create public and private subnets, develop dApps, and do it fast, cheaply, and with a high level of security.
Avalanche vs. Ethereum
In the crypto community, Avalanche is called a major rival to Ethereum because it processes transactions quickly and cheaply. Let's compare.
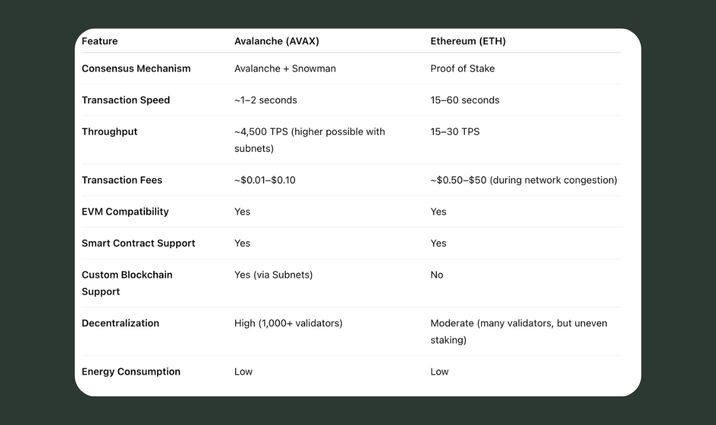
As you can see, Avalanche is definitely faster and cheaper than Ethereum. This can be explained by how its consensus mechanism works.
How the Snowman Algorithm Works
Avalanche uses a family of consensus protocols called “Snow”. It includes three consensus mechanisms: Avalanche, Snowman, and Frosty.
The Avalanche consensus mechanism doesn't use blocks because it relies on parent transactions called vertices. These allow validators to group transactions for voting. To determine transaction validity, validators send each other responses randomly. The confirmation process occurs in stages over a series of rounds.
Snowman was developed based on Avalanche. It orders transactions linearly and creates blocks instead of vertices. This allows the network to work with smart contracts and increase network capacity.
To date, the project team has implemented Snowman on the P-Chain and C-Chain blockchains and Avalanche on the X-Chain network. Frosty is in development.
How the Avalanche Consensus Mechanism Works
Unlike Bitcoin and Ethereum, the Avalanche Consensus Mechanism doesn't require everyone in the network to come to an agreement at the same time. Instead, Avalanche uses random samples of nodes that quickly negotiate with each other. This process is repeated until there is enough agreement. Let's look at this approach using colored circles.
For example, nodes are assigned colors: blue or yellow. Suppose a node is yellow and makes a request to five random nodes (shown as red rings in the picture). If most of them are blue, the node changes its color and becomes blue. This process is repeated until all nodes become one color.
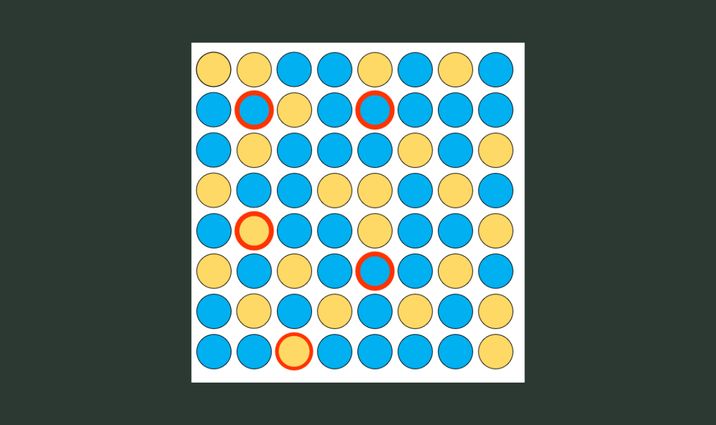
The algorithm determines nodes randomly, but the chance of participating in transaction verification increases as the amount of staked Avalanche tokens increases.
What role does AVAX play in the ecosystem?
AVAX is the native token in the Avalanche blockchain. As of May 2025, there are approximately 418 million AVAX in circulation, which is about 58% of the maximum supply. The protocol burns all transaction fees, making AVAX a deflationary asset.
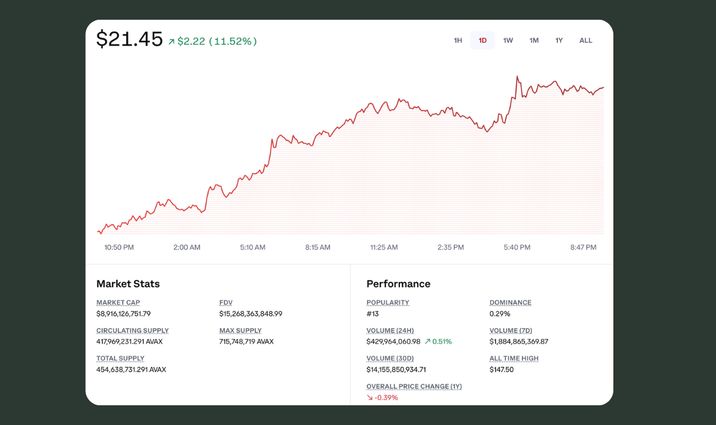
You can use the token for staking (APY is about 7.60%), fee payment, and operations on the Avalanche subnets. Of course, you can also buy, sell, send, receive, and swap AVAX in Coin Wallet.
How to find an AVAX transaction ID
A transaction ID, or TXID, on the Avalanche network is an alphanumeric string of 66 characters. It looks like this:
- 0xf5845644f9ec13e1baffb429eeee9308bbb5d27dbd2ce251ec601b549fddd962
- 0x0fa7415da71bdf249854ca7b515d8183ca3374b69952bebb04b9e0ba38e914d3
There are two ways to find a transaction ID.
- The first way is to use a blockchain explorer such as Snowtrace Multichain Explorer. Just enter your wallet address or the name of the token in the search bar.
- The second way is to check the “History” section in Coin Wallet. Select the coin from the coin list and open the “History” section.