What is Cardano? A Closer Look at Cardano

Over the past week, Cardano (ADA) has significantly strengthened its position in the cryptocurrency market. The ADA price is currently around $0.7296, reflecting an increase of about 16.1% for the week. At the same time, the coin is often considered to be “forever under development”, and its creators are said to overpromise new features. In this article, we decided to find out what Cardano is, how to find its transaction ID, and why it’s considered one of the most reliable blockchains on the market.
What is Cardano?
How does the Cardano algorithm work?
Why is Cardano often compared to Ethereum?
How to find an ID transaction?
Why does the crypto community criticize Cardano?
What is Cardano?
Cardano is a blockchain that was designed to conduct transactions and create smart contracts. It might be called a more advanced version of Ethereum. This is the only blockchain that has an academic foundation. It is developed by scientists and engineers, and each update is scientifically tested.
The thing is, Cardano didn’t start with a loud ICO or speculation. First, they spent several years writing papers, doing research, and mathematically proving the system’s security — only then did they launch the blockchain. This is completely different from many other projects that first create a token and only later figure out how it should actually work.
They follow the principle of “peer-reviewed first, code later” — meaning everything goes through academic review before it’s implemented in code.
Before implementing any technology on the Cardano blockchain, the team — mostly from the company IOHK, founded by Charles Hoskinson — develops detailed technical documents. These documents explain how and why new features — such as staking or voting systems — will work. After that, each document goes through an expert review.
The native coin of Cardano is called ADA, named after Ada Lovelace — the first computer programmer. Within the Cardano network, ADA is used to pay transaction fees, participate in governance, and earn rewards through staking.
The Cardano architecture is built on two layers. The first one simply transfers money, while the second layer manages the logic — these are smart contracts. This makes the network more flexible and easier to update than, say, Ethereum.
How Does the Cardano Algorithm Work?
Cardano’s standout feature is its unique consensus algorithm, Ouroboros. This is a type of proof-of-stake algorithm, but it works differently from others. Unlike other blockchains, Cardano first developed and peer-reviewed the Ouroboros algorithm within the academic community — publishing it before implementation.
The Ouroboros algorithm divides time in the blockchain into two main structures:
- Epochs — long periods of time (about 5 days on Cardano’s mainnet).
- Slots — short intervals (1 second in the current implementation).
Each slot may have a designated slot leader — a participant eligible to produce a block during that time. To choose who will create a block in each time slot, Cardano’s algorithm uses a probability model based on how much ADA you own or how much has been delegated to you.
Here’s how it works:
1. Stake Distribution Snapshot
Before every new epoch, the network takes a snapshot of how ADA is distributed — meaning who holds how much and how much is delegated.
2. Leader Election Function
Then, for each time slot, the network needs to figure out, "Who will create the block?" This is done using a secure cryptographic function. Each participant with enough ADA runs a check on their own computer using a VRF (Verifiable Random Function).
This function gives a number between 0 and 1. If that number is below a certain threshold, you become the slot leader (you get to create the block).
The threshold depends on your stake size — the more ADA you have (or have been delegated), the higher your chances.
This process is fully decentralized — everyone checks for themselves whether they won the slot. There’s no central authority choosing winners.
For example, if you own 2% of the total ADA in the network, you have a 2% chance to be chosen as leader for any given slot. The algorithm checks this locally using the VRF. If you win, you create and sign the block, then broadcast it to the rest of the network.
Therefore, Ouroboros is a product of dozens of researchers and years of work, and one of the most rigorously researched protocols in the blockchain world.
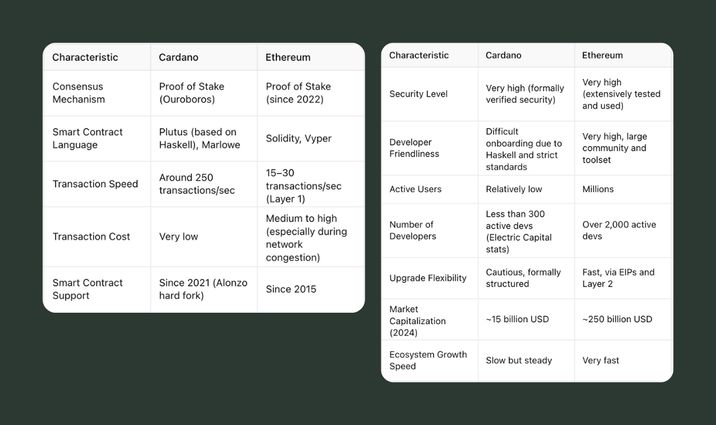
Why is Cardano Often Compared to Ethereum?
Cardano was created by Charles Hoskinson, who was one of the co-founders of Ethereum. According to public reports, he left the company because of disagreements over whether the project should remain non-profit, as Vitalik Buterin envisioned, or follow a for-profit business model. Hoskinson chose the second path and left to build “the next level of blockchain,” but this time by his own rules.
As a result, Cardano is often compared to Ethereum, and we are no exception.
How to Find a Transaction ID
A transaction ID is a SHA-256 hash (sometimes Blake2b in some tools). It is created using all the data in the transaction — including inputs, outputs, signatures, metadata, and other details.
It looks like a hexadecimal string — made up of numbers (0–9) and letters (A–F).
The ID usually has 64 characters:
- b347d746f16f9f23f84b720f52864c69fb606cdef26226002c9640b101c4c245
- d67c7c549024490b0a14547ee07dcf6533397316baa65175fb88d256887c2dcb
There are several ways to find transaction IDs:
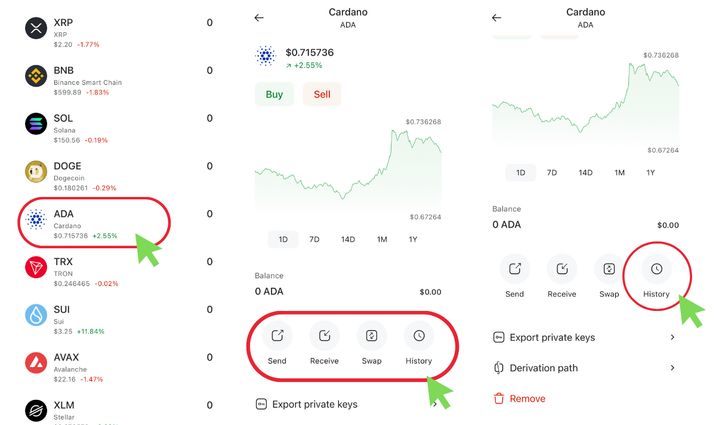
1. In your wallet. For example, in Coin Wallet, just select the coin from the list and go to the ‘History’ section.
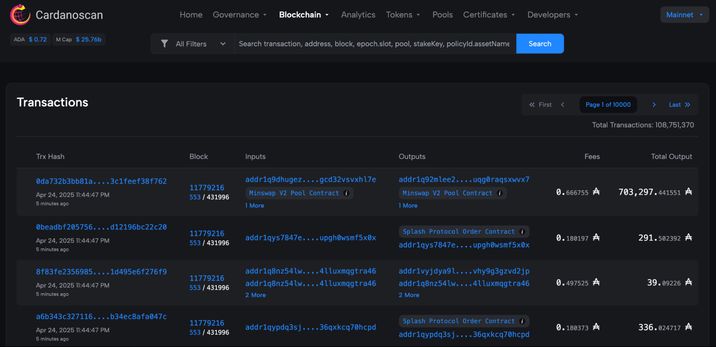
2. In blockchain explorers. There are several platforms: Blockchair.com, Cexplorer.io, and Cardanoscan.io. You can find more options on the official Cardano website.
Why does the crypto community criticize Cardano?
Cardano is often criticized for moving too slowly. Because of its scientific approach, every update goes through academic research, peer review, formal verification, and testing on a testnet — only then is it added to the main network.
This makes the network very reliable, but competing blockchains like Solana, Avalanche, or even Ethereum 2.0 have already launched many features that are still being discussed in Cardano. As a result, Cardano often seems like it’s “always in development.”
Despite supporting smart contracts since 2021, the Cardano ecosystem has few real-world applications: there are not many DEXs (decentralized exchanges), not many NFT marketplaces, and user activity is relatively low.
In other words, Cardano is being built like a Swiss watch — precise and reliable — but sometimes people just want a technology that works.