Atomic Swaps Introduction

Atomic Swaps are a way for users to exchange cryptocurrencies without the need for a third party, such as an exchange. They provide an alternative to centralized exchanges as they offer increased flexibility for trading altcoins and do not have associated exchange fees.
Currently, there is a lot of friction when you want to exchange one altcoin into another. First you may have to give up custody of your cryptocurrencies by depositing them to a centralized exchange. The exchange may not offer the specific trading pair you would like to trade so you must exchange into an alternative coin that can be traded directly with your cryptocurrency of choice. This process can be slow and has many drawbacks, including fees and third party and counterparty risk. Atomic swaps solve these problems.
What are Atomic Swaps and What Problem do they solve?
The term “Atomic” derives from Computer Science and means indivisible. The Computer Science definition is as follows: Either the operation is conducted as planned or else it is not conducted at all.
In practice, this means that I will either exchange my cryptocurrency with the other party, exactly how we agreed, or it will not happen at all. Hence, Atomic Swaps remove the possibility of human error or manipulation.
Atomic Swaps form the basis of a trustless secure exchange of cryptocurrencies without the need for a centralized exchange or intermediary. They provide the framework for trustless exchanges of altcoins as well as eliminating exchange fees.
In 2013 Tier Nolan first thought of an idea of peer-to-peer swaps without the need or intervention of a third party. This technology was brought to life by Charlie Lee in 2017. The founder of Litecoin tweeted that he had successfully executed a cross-chain atomic swap with LTC to BTC. He exchanged 10 Litecoins for 0.1167 Bitcoin. Pretty good trade considering at the time this article was written BTC = $56k and LTC =$185.
Both Tier Nolan and Charlie Lee proved that cross chain Atomic swaps were possible.
Today, Atomic swaps offer the potential to change how cryptocurrencies are traded and are poised to play a crucial role in the ecosystem. They can be used to reduce friction and increase flexibility when trading altcoins as they facilitate cross chain trades. This allows users to exercise complete control over their wallets.
How Atomic Swaps Work (HTLC)
So how Atomic swaps work? Atomic Swaps leverage Hash Time locked contracts. HTLCs are smart contracts that lock the cryptocurrencies involved in the transaction and require verification from both parties to release the funds and complete the exchange.
HTLCs are comprised of two components:
- Hashlock
- Timelock
A hashlock is a cryptographically scrambled version of a public key. It is generated by the originator of the transaction. The private key is then used to unlock the original hash. The originating party then generates the key and hashes it, storing the hash in a pre-image that is revealed during the final transaction.
Funds are locked in smart contracts that can be publicly inspected on the blockchain. The funds can only be released with the pre-image that matches the hash of the contract. If either party wants to cancel the transaction, they can just walk away and the funds will be returned to the original owners.
The time lock component is a function within HTLCs that defines the time allowed for the transaction to be completed by both parties before the cryptocurrencies are returned to their respective original owners. This time period is called the “withdrawal time” and the function prevents cryptocurrencies from being locked into the smart contract if either party does not complete their transaction.
HTLCs are the backbone of Atomic Swaps and are responsible for many of the favourable properties of Atomic Swaps, such as the trustless nature and the absence of exchange fees.
Example of How Atomic Swaps Work
If you want to exchange altcoins ordinarily you would use a centralised exchange. However, these come with a host of risks and problems such as; Hack Vulnerability and Mismanagement. A famous example of these issues coming to the fore was the Mt Gox robbery where $500 million of Bitcoin was robbed in 2014.
Atomic Swaps provide an alternative to centralised exchanges. Let's suppose Lucy wants to exchange Bitcoin into Litecoin and Dave wants to exchange Litecoin to Bitcoin. They agree to transfer via Atomic Swap at an agreed upon exchange rate. A HTLC is then created via their Atomic Swaps Wallet.
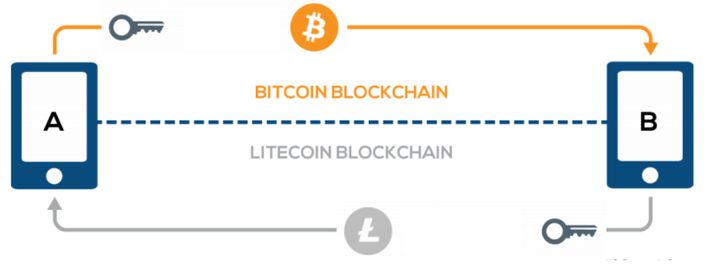
When Lucy deposits her BTC into the HTLC address a hash is created. This hash works like a lock to a virtual safe. Lucy also generates a key in the form of a datastring.
Lucy then sends the hash to Dave in order for Dave to fulfill his obligations in the contract.
Dave follows the same steps as Lucy and deposits his Litecoins in a contract address using the same hash as Lucy.
Both funds are now locked with the same key. When Lucy receives the Litecoins from Dave’s address she can unlock it using the key. The key is then revealed to Dave (at the same time that Lucy uses the key to unlock the Litecoins), allowing him to access the Bitcoin funds.
This means that Lucy cannot receive the Litecoin Dave locked up without revealing the key to Dave. This creates a trustless transaction. Neither party can gain access to the other party's funds without the transaction being completed.
If the transaction is not completed within the given time period the locked up cryptocurrencies will be returned to their respective owner.
This may occur in the event that either Dave or Lucy do not deposit their cryptocurrencies within this time period.
In this example, we used Bitcoin and Litecoin.However, Atomic Swaps have cross chain functionality meaning that any two altcoin pairs can be exchanged.
This is possible as the transaction consists of two smart contracts, one on each chain, allowing for the exchange of any altcoin combination.
What Perks do Atomic Swaps Offer?
Atomic Swaps provide users with 3 main benefits:
- No trading fees
- Security
- Choices when trading Altcoins
The image below outlines the market maker and taker fee associated with trading on some of the major centralised crypto exchanges:

Atomic Swaps are the infrastructure that allows for the formation of a trustless feeless exchange of cryptocurrencies.
When trading altcoins, users often paid high trading fees when using centralized exchanges and they were often restricted by the trading pairs offered. Atomic Swaps remove some of the risks and pain points associated with trading altcoins and provide an alternative to centralized exchanges.
One of the limitations of Atomic Swaps is that they are not compatible with fiat currencies and hence you can only exchange from one cryptocurrency into another.
Don’t Decentralized exchanges solve the problem with centralized exchanges?
In short, No, Decentralized exchanges only allow for the exchange of cryptocurrencies on the ## same blockchain. Atomic Swaps can facilitate the exchange of cryptocurrencies on different blockchains.
This cross chain functionality allows for increased choice when selecting what cryptocurrency you would like to exchange.
What Chains Are Supported And Future Implementation
Many believe the Atomic Swaps will be used in conjunction with the lightning network to facilitate instant, feeless, and trustless transactions between cryptocurrencies.
Companies like AtomicDex (https://atomicdex.io/) are currently developing an Atomic Swaps exchange. It is widely expected that companies like AtomicDex, will develop user wallets and interfaces for Atomic Swaps that streamline the process of trading altcoins.

The open source platform ,Komodo, is playing a crucial role in the future implementation of Atomic Swaps. Komodo’s lead developer, jl777, wrote the code that allowed some of the first Atomic Swaps to take place.
Komodo’s Atomic Swap technology now supports 95% of all coins and tokens in existence.
BarterDEX is the decentralised exchange associated with Komodo.

Komodo is currently leading the industry in terms of Atomic Swaps.
Conclusion
As the cryptocurrency becomes more mainstream, there will be more emphasis placed on the cross chain exchange of cryptocurrencies, and Atomic Swaps will inevitably play a leading role. They have the potential to completely revolutionize money transfer in the crypto space.
Atomic Swaps outperform traditional centralized exchanges in terms of fees and do not pose the same counterparty and third party risks. They are a trustless exchange mechanism built using smart contracts, HTLCs, and provide the infrastructure to seamlessly exchange altcoins.
Atomic Swaps remain relatively new, having been first demonstrated in 2017; however, they have the potential to become a very important function in the cryptocurrency space in the coming years.