Decentralised Finance - Defi

What is DEFI?
Decentralized finance, or DeFi, is the concept of recreating financial instruments using cryptocurrency and decentralised blockchain technology.
DeFi is aiming to replace a lot of traditional finance tools we use each day such as borrowing, earning interest on deposits and lending. DeFi applications differ from traditional banks and financial services providers in the sense that there is no third party involved. Therefore, many of the fees associated with third party providers no longer apply as the process is now decentralized and anonymous.
DeFi applications are built using smart contracts. Typically these applications run on the Ethereum blockchain.
The national average annual percentage yield or APY on savings accounts in the US today is a mere 0.04%.
Much higher interest rates can be achieved using various DeFi platforms and more competitive borrowing rates can be achieved by borrowers. For example, to borrow ether from the Aave platform, has a current interest rate of 0.16%. Borrowing ether from Compound, the interest rate is 2.88%. This makes DeFi an ever more attractive alternative to traditional financial services providers.

Risks associated with DeFi
Earning high interest rates and profiting from Decentralised Finance comes with elements of risk. Decentralised Finance is a relatively new concept in comparison to traditional financial services providers. This new technology and innovation potentially comes with risks associated. DeFi is still highly experimental and potentially exists in a regulatory grey zone as regulators have not caught up to the innovation.
Bad actors may also be attempting to exploit the new excitement and enthusiasm in the industry by creating projects with no track record and no value.
In the US there is no FDIC insurance protection for your money when using DeFi. This can be a significant off putting factor on whether or not someone uses a decentralised finance application. DeFi applications and cryptocurrencies rely on the blockchain they run on. Some analysts believe this may pose a systemic risk.
However, DeFi does carry some inherent risks due to it being a new technology but some of the potential risks in my view are outweighed by the known benefits of using and participating in decentralized finance. DeFi has the opportunity to disrupt the financial sector in a way we have never experienced. It has the potential to replace many financial services companies and provide a more equitable and fair financial system for everyone.
Who are the players in DEFI?
There are 3 major players in the DeFi space at the moment. They are Compound, Aave and Uniswap. The account for nearly $44 Billion in “locked up” cryptocurrency.
Compound
Compound was founded as a decentralized money market protocol based on the ethereum blockchain. The platform allows users to borrow and lend digital assets by using their crypto as collateral. To earn interest on your cryptocurrencies you can add them to the liquidity pool and earn compound interest on your crypto. The interest rates achieved are determined by the supply and demand of the specific crypto currency. These rates adjust automatically.

COMP is the native token on Compound. COMP is a governance token on the Compound platform. It is used to practice a type of on-chain governance. If a user holds at least 100,000 COMP they are able to make proposals for the network to consider.
If enough COMP holders vote for the proposal then a proposal is passed and enacted.
COMP tokens can be bought on almost all major crypto exchanges including coinbase.
Compound sets aside 10% of interest paid as a reserve with the remainder going to the liquidity providers. The protocol has over $10 Billion locked up in its liquidity pools. This makes Compound one of the biggest DeFi platforms on the market.
Aave
Aave is a decentralized, non-custodial liquidity market protocol. What does that even mean? It means that users can participate as lenders or borrowers of cryptocurrency where the lenders provide liquidity to the market and earn passive income in the process. Borrowers can obtain over collateralized and under collateralized loans meaning they have the ability to select how much collateral they put up for a given loan. This will ultimately determine the interest rate.

Aave provides trustless, uncollateralized loans where borrowing and repayment are made in the same transaction.
The native governance on the Aave protocol is AAVE. However, the platform can provide support for 16 different digital assets.
Aave has some prominent backers:

They currently have over $14 Billion in locked up digital assets.
Uniswap
Uniswap is a decentralized exchange that offers users the ability to swap between ETH and ERC20 tokens on-chain or earn fees or interest when providing cryptocurrency to liquidity pools.
The conversion of ERC-20 tokens is facilitated by an easy to use UI:
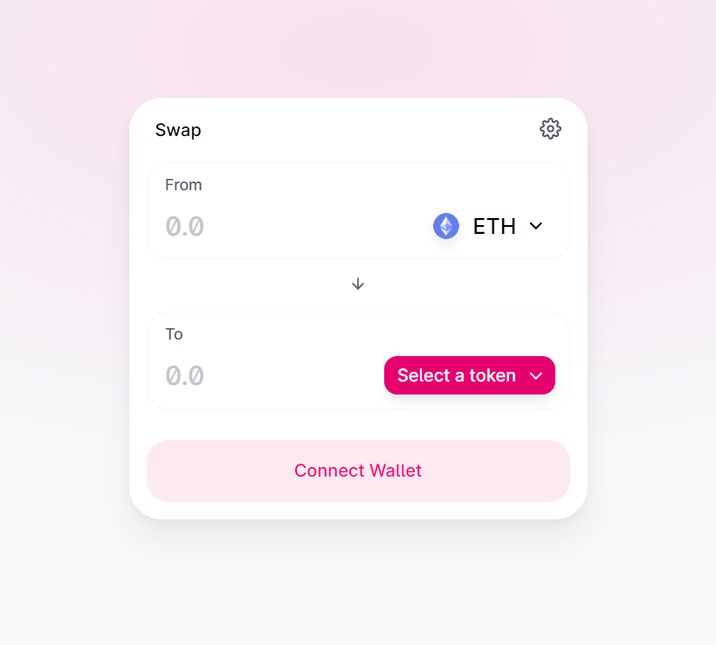
Uniswap enables the ability of users to create markets and help improve the exchange liquidity by providing interest in return.

There are currently more than $4 Billion worth of ethereum tokens held in Uniswap liquidity pools.
What is yield farming?
Yield farming is sometimes referred to as liquidity mining. It is a way of generating rewards using your cryptocurrency holdings. Put simply, yield farming is a way of obtaining rewards for locking up your cryptocurrencies.
Yield Farming is similar to staking however, there is a lot more complexity when you drill down on the process behind yield farming. Users can become liquidity providers by locking their cryptocurrencies into liquidity pools.
Liquidity pools are essentially a smart contract that contains crypto funds. In return for providing liquidity you get rewarded. Some liquidity pools pay their rewards in multiple tokens. Those reward tokens can then be deposited into other liquidity pools and so on.
It becomes clear that this strategy can quickly become more complex and intricate. Yield farming is typically carried out using ERC-20 tokens built on the Ethereum blockchain.
In the future there will be cross-chain bridges that may allow DeFi applications to become blockchain agnostic. This would result in a large increase in the capabilities of these applications and offer more flexibility to yield farmers.
Yield farmers typically move their funds in search of the highest yield. This may involve moving your funds to a different protocol.
Can you get a loan from crypto?
Crypto loans are collateralized loans which means borrowers offer some of their crypto as collateral.
A borrower first obtains a fiat loan from a lender in lieu of their crypto holdings. This acts as a security in the absence of repayment of the loan.
Once an interest rate is accepted between the borrower and the lender the exchange of crypto is executed. The borrower then must pay the lender back and once the loan is paid in full the collateral is released.
Crypto loans also facilitate the borrower to use fiat to get a loan in a cryptocurrency.
Crypto loans are carried out on DeFi lending platforms where the lenders and borrowers interact without the requirement of an intermediary.
What is the future of DeFi?
The primary objective of DeFi is to provide fast, secure, cheap and fair financial services to everyone. At the moment DeFi still carries many risks although its promise is obvious.
As the technology powering DeFi becomes more mature and sophisticated these risks will decrease as there will be an even stricter adherence to both legal and regulatory frameworks. This will legitimize the space even further.
At its core DeFi is aiming to improve financial services for all and is sure to play an ever increasing role in the new financial system.