What Is Bitcoin's Lightning Network?

When Bitcoin was launched, not everyone anticipated that it would grow to be one of the world’s most important investments. With its growth, its network becomes more congested. A block of BTC transactions is verified once in 10 minutes. When the network becomes too crowded, transactions may take a long time until they are verified. Simultaneously, this traffic makes transaction fees more expensive. If you want your transaction to be verified faster, you should pay more fees. This scalability issue is one of the few problems that Bitcoin has as the world’s biggest cryptocurrency. However, there is actually a solution to this problem that is becoming one of the reasons why Bitcoin can potentially outgrow its all-time high. Such a solution comes from Bitcoin’s Lightning Network.
Bitcoin’s Lightning Network is a network within Bitcoin that is still evolving as a concept and helps maintain high scalability in microtransactions for Bitcoin. This article focuses on the fundamentals of this network and what it means for Bitcoin in the long term. It is important that you know about the Lightning Network so that you may know how to utilize it and how it can affect the future price of BTC. So, let’s begin with the key elements of this network so that you have a brief idea about it.
What is the Lightning Network
Bitcoin manages to confirm 7 transactions per second. While this may seem enough, it is slightly low when compared to other payment options. Bitcoin Cash manages to record 61 transactions per second. Visa, on the other hand, manages to record more than 20,000 transactions per second. This is considerably more efficient than Bitcoin.

As suggested, this low number of transactions per second can make Bitcoin inefficient, slow, and expensive. After many attempts to solve such an issue, the proposal for a new network within Bitcoin that focuses on microtransactions can finally resolve the scalability problems. This is where Bitcoin’s Lightning Network comes in.
The Lightning Network is a layer 2 solution in the Bitcoin network. The main idea of this second layer in Bitcoin’s network is that not every transaction needs to be verified. Sending small amounts of BTC to your friend that you trade with constantly should not be tracked every single time. Instead, once you finish your micro trades with your friends, you notify the blockchain about the final version of your addresses. This happens by creating a multi-signature wallet, where two different addresses are involved in creating it.
Bitcoin’s Lightning Network was proposed by Joseph Poon and Thaddeus Dryja back in 2015 in a white paper. To maintain such a network, three main teams continuously work in the development aspect. These are the Blockstream, Lightning Labs, and ACINQ. They are also constantly helped by experts from the Bitcoin community that support the Lightning Network.
With their own implementations of the network, Bitcoin’s Lightning Network is one of the most complex layers in a cryptocurrency. While it is constantly evolving, it has been a great step towards the scalability issues of Bitcoin, especially for smaller traders.
How Does It Work
The best way to explain the Lightning Network is by taking a hypothetical example. Let’s say that person A and person B want to constantly trade with one another in small amounts. Trading smaller amounts still takes time and costs a lot of money because of network congestion. Both people A and B can create a multisignature wallet. This multisignature wallet requires that they deposit a certain amount of BTC in their multisignature wallet that they plan to use for microtransactions. Let’s say both of them deposit 0.5 BTC each in the wallet. They now have 1 BTC in their multisignature wallet. In layer 2, the lightning network, person A and B can trade between each 0.5 BTC that they deposit. Person A can send 0.1 BTC to person B, and then they may have 0.4 BTC and 0.6 BTC respectively. Then, person B can send 0.3 BTC to person A so that person A would have 0.7 BTC and person B 0.3 BTC. This can go on for as long as the two want. In simple words, they can trade the deposited amounts in the multisignature wallet how many times they want without having to pay any transaction fee.
So how are the transactions verified in the first place? The microtransactions in the Lightning Network are not verified at all. Instead, the blockchain records the initial amounts that person A and B deposited when they created the multisignature wallet. Whenever person A and B decide to close the multisignature wallet and withdraw the BTC from it, the blockchain records the final amount of BTC that person A and B have. So if both started with 0.5 BTC each, the network would check their final amounts (i.e. 0.7 BTC and 0.3 BTC respectively) and verify that. So all the microtransactions that occurred after the multisignature was opened and before it was closed do not need to be verified, saving both people A and B money from the omitted transaction fees, and saving them time from the omitted need to verify transactions.
The good thing about the Lightning Network is that it does not have to be only about two people. If you have a multisignature wallet with someone, and he/she has a multisignature wallet with another one, you can directly trade with the latter person without creating a multisignature wallet with him/her. Using this system, a network full of people who are connected with one another is formed. In other words, the Lightning Network is another network within the main Bitcoin network that allows users to directly trade smaller amounts of BTC instantly and without having to pay fees.
The implementation of the Lightning Network can finally make Bitcoin an efficient payment method for daily transactions, such as buying a soda at your local market. Previously, since Bitcoin has grown so much, buying something at a store would take minutes until it would be verified, and you would have to pay more than the required amount because of transaction fees. Now, with the Lightning Network available, you can create a multisignature wallet with the store where you can deposit a certain amount of BTC, while the store deposits 0 BTC. In this way, you can make instant payments and not pay additional fees whenever you would use BTC to buy something from the store.
The Lightning Network is designed in such a way that only microtransactions are supported. Since it is a second layer in the Bitcoin network, it does not have the same level of security as Bitcoin has. This inclines people to deposit only smaller amounts.
As the Lightning Network receives more attention and develops as a concept, cross-chain Lightning Networks are made possible. Users can trade different cryptocurrencies using the Lightning Network in the same way. However, if the Lightning Network is a huge success, it would be bad news for cryptocurrency exchanges, which are the main trading station for investors, whether that is for small or big transactions.
Pros & Cons
As fascinating as it may sound, the Lightning Network has both advantages and disadvantages since it is still in its infancy.
Pros
- First and foremost, transactions are instant even if the network is crowded. Such a feature is the pillar of the lightning network and is the solution to the scalability issues in the Bitcoin network. Technically, 1 million BTC transactions can be conducted per second in the Lightning Network.
- Transaction fees are omitted since the microtransactions within the Lightning Network do not need to be verified. The implementation of the Lightning Network can make BTC payments for daily transactions (i.e. drinks, food, etc) affordable and efficient.
- Anonymity is another advantage that the Lightning Network provides. Since microtransactions in the network do not need to be verified, no one keeps track of who sends BTC to whom. All that needs to be verified is the initial and final amounts in the network.
Cons
- There are still fees that need to be paid for opening and closing the multisignature wallet. While microtransactions within the Lightning Network are cost-free, you need to pay whenever you open and close a multisignature wallet since the blockchain needs to verify the initial and final versions of your wallet.
- The Lightning Network requires that users remain online at all times when using a multisignature wallet. If one node goes offline, the other node can close the multisignature wallet without the consent of the other. Furthermore, continuously remaining online makes you more vulnerable to online hackers. This can perhaps be avoided by using cold wallets.
The Current State of the Lightning Network
Now that we have explained the Lightning Network, let’s look at where it stands today.
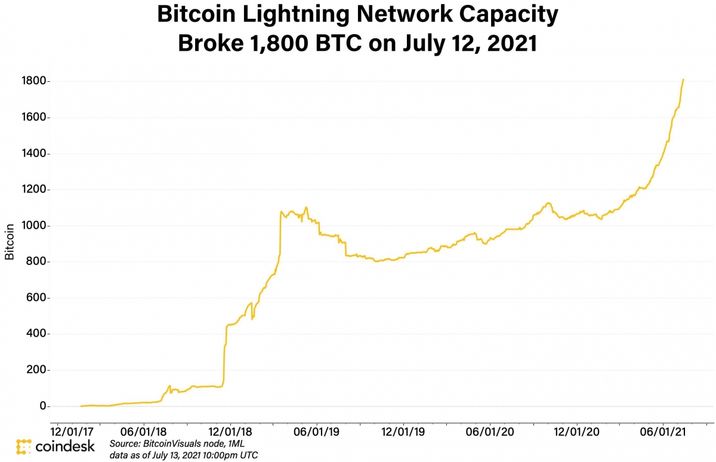
As of July 2021, the network has exceeded 1,800 BTC. This growth showcases the increase in usage of the Lightning Network over the years.
With that said, there are more than 22,000 nodes and more than 56,000 channels in the network. These numbers have increased massively in recent months. One reason for this is the adoption of Bitcoin in El Salvador as legal tender. Moreover, companies such as Strike have started to use the Lightning Network because of the efficiency it provides.
A recent addition in the Lightning Network from the Lightning Lab is a liquidity pool that can be available in the channels of the network. This incentivizes users to use the Lightning Network and be liquidity providers in the Lightning Network. They can earn additional BTC as a reward.
Overall, the Lightning Network looks like it is going to keep growing in the next few months, potentially reaching 60,000. This only shows how much success this network has had and how much it can keep growing. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies can finally be used for microtransactions in an efficient manner. As the CEO of Lightning Labs Elizabeth Stark said, “It’s no longer just the future. Lightning is here.”
Takeaways
- Bitcoins Lightning Network is a layer 2 blockchain in Bitcoin that allows users to do microtransactions without having to pay additional fees and wait for them to be verified.
- A multisignature wallet by two users needs to be created for them to be able to use the Lightning Network.
- Fees still need to be paid when opening and closing the multisignature wallet.
- The Lightning Network today is one one the biggest networks working on a blockchain.