How to Reduce Crypto Transaction Fees in 2026

Hi crypto fans 💲
One of the biggest challenges in the crypto world is dealing with transaction fees. While privacy concerns can often be addressed through technological innovation and regulation, fees depend on many dynamic factors. For example, in August 2025, the TRON team updated its fee calculation model in response to severe network congestion and rising costs. And TRON is just one example — users across Ethereum, Bitcoin, and other networks regularly struggle with high costs.
To reduce these expenses, many users look for more affordable ways to send transactions. For instance, on the Ethereum network, it’s possible to reduce gas fees by transacting at night, when the network is less loaded.
Fortunately, this isn’t the only strategy. In this article, we’ll explore additional methods to help you reduce crypto transaction fees in 2026 — including using Coin Wallet and switching to more efficient networks — all without compromising security or speed.
What Are Crypto Transaction Fees?
When sending or exchanging cryptocurrency, users typically encounter several types of fees — and understanding them is key to optimizing your costs. So, how much does it cost to send crypto? It depends on the network, the platform, and the transaction type.
The most common types of fees include:
- Network fee (transaction fee) — a base fee required to process your transaction on the blockchain. It goes to the miners or validators who confirm and secure the network.
- Gas fee — specific to Ethereum and other smart contract platforms, this is a variable fee paid to execute operations — like transfers or interactions with dApps. The gas cost changes based on network congestion and transaction complexity.
- Miner fee / validator fee — often used interchangeably with transaction fee; this is the reward paid to those validating the transaction.
- Withdrawal fee — charged by exchanges or platforms when transferring funds out of your account to an external wallet. This fee is platform-specific and not tied to the blockchain itself.
Read more about the type of crypto transaction fees in our special guide.
While people often confuse the terms, there’s a key difference between transaction fees and gas fees. A transaction fee is a general term used across blockchains (e.g. Bitcoin, Litecoin), usually fixed or predictable. A gas fee, on the other hand, is dynamic and unique to smart contract networks like Ethereum — it reflects how much computation your action requires.
7 Proven Ways to Lower Crypto Transaction Fees
1. Use Layer 2 Networks
One of the most effective ways to reduce Ethereum gas fees is by using Layer 2 (L2) networks — blockchain solutions built on top of Ethereum that handle transactions off-chain and then settle them on the main network.
Layer 2 networks like Arbitrum, Optimism, and zkSync significantly lower transaction costs by reducing the amount of computation and storage required on Ethereum’s base layer. While a typical on-chain transfer might cost several dollars during periods of high congestion, L2 networks can process the same transaction for a fraction of the cost.
These solutions are ideal for users who want to avoid Ethereum gas fees without leaving the Ethereum ecosystem. Most L2s support standard wallets, and many decentralized apps are already integrated with them.
2. Choose Cheaper Blockchains
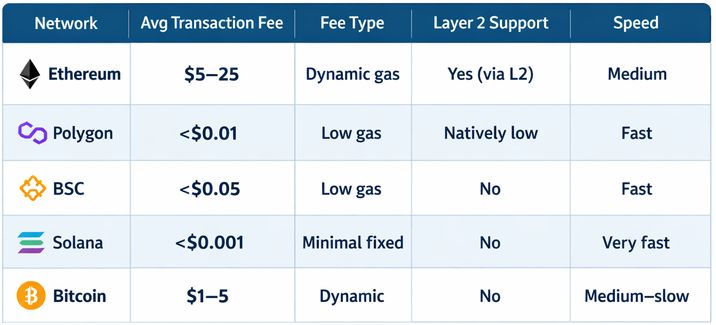
Another effective way to lower transaction costs is by choosing a cheaper blockchain network. While Ethereum remains the most widely used smart contract platform, it’s not the most affordable — especially during periods of high activity.
Alternative networks like Polygon, Solana, and Binance Smart Chain (BSC) offer much lower fees for everyday transactions. For example, while sending tokens on Ethereum may cost several dollars, the same transfer on Polygon or BSC can cost just a few cents. On Solana, fees are often a fraction of a cent.
If your transaction doesn't require Ethereum specifically — for example, if you're sending stablecoins or transferring assets between wallets — using the cheapest crypto network available can help you avoid unnecessary gas costs.
3. Use a Low-Fee Wallet
The choice of wallet can also impact how much you pay in transaction fees. Some wallets are optimized for cost-efficiency, while others may apply additional service fees or provide limited options for network selection.
A good low fee crypto wallet should allow you to choose between different blockchains, customize transaction parameters like gas limits, and avoid hidden platform fees. Wallets that support Layer 2 networks or cheaper blockchains (like BSC or Polygon) offer additional savings.
For example, Coin Wallet supports multiple networks and allows you to choose any coins for reasonable fees. In contrast, some custodial or exchange-based wallets may include fixed withdrawal fees, regardless of network conditions.
4. Track Gas Prices
Gas prices on networks like Ethereum can fluctuate dramatically depending on network activity. Sending a transaction during periods of high demand — such as during major NFT drops or market volatility — can cost significantly more than during quieter times.
To avoid overpaying, it’s helpful to check a gas tracker crypto tool before initiating a transaction. These tools show current and predicted gas fees, helping you choose the optimal time to send.
Some of the most popular gas tracking tools include:
Most gas trackers categorize fees as "low," "average," or "high," and also show estimated transaction times. If your transfer isn’t urgent, simply waiting for fees to drop can save you money — especially on Ethereum.
5. Send at the Right Time
Crypto networks don’t operate on a fixed schedule — their transaction fees fluctuate based on activity. That’s why choosing the best time to send crypto can significantly reduce your costs, especially on high-demand blockchains like Ethereum.
In general, fees tend to be lower during off-peak hours — typically late at night (UTC) or on weekends, when fewer users are active. These periods see less congestion, which directly affects gas prices and confirmation speed.
For example, sending a transaction on a Saturday night may cost up to 50% less than during weekday business hours. This strategy works well for non-urgent transfers, where a slight delay is acceptable in exchange for lower fees.
Pairing this approach with a gas tracker gives you even better control over timing and costs.
6. Batch Transactions
If you regularly send multiple crypto transactions — for example, to employees, customers, or multiple wallets — you may benefit from batching. This means grouping several transfers into a single transaction, which can significantly reduce fees on supported blockchains.
Some platforms and protocols allow batch crypto transactions, where a single on-chain operation processes multiple payments at once. Instead of paying a separate network fee for each transfer, you pay once for the batch, which lowers the average cost per recipient.
This method is especially useful for crypto businesses, payroll operations, or treasury management. However, it requires specific wallet or platform support — not all services offer native batching features.
7. Avoid Expensive On-Chain Swaps
Swapping tokens directly on decentralized exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap or SushiSwap can be convenient, but also costly — especially on networks like Ethereum. On-chain swaps often involve high gas fees, price slippage, and sometimes multiple contract interactions, which all add to the final cost.
To reduce these expenses, many users opt for centralized exchanges (CEXs) or aggregators like 1inch or Matcha, which route trades through the most cost-effective paths. These platforms can offer better rates, lower execution costs, and allow for off-chain settlement, reducing gas usage.
Another option is to use wallets or apps that integrate with Layer 2 DEXs or support off-chain swaps. These solutions help minimize both fees and slippage, especially when trading large amounts or during peak network activity.
If you're looking to optimize every aspect of a transaction — not just sending, but also exchanging — avoiding expensive on-chain swaps can make a noticeable difference.
Which Networks and Wallets Have the Lowest Fees?
Fees can vary significantly depending on the blockchain network and the wallet you use. Below is a comparison of major networks and their average transaction fees. We also created Coin Wallet’s ultimate guide to compare some ways to reduce crypto fees.
Blockchain Network Fee Comparison
Wallet Fee Comparison
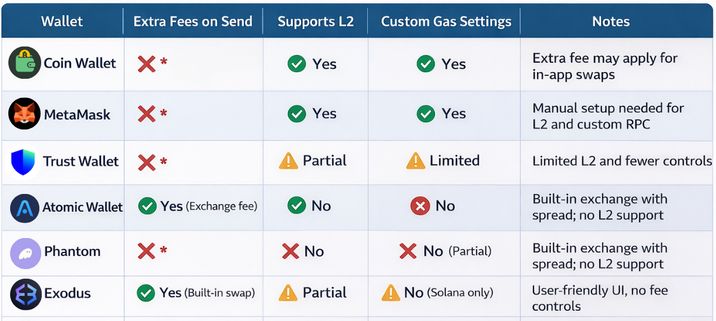
Not all wallets are created equal when it comes to fees. Some offer full control over gas settings and network choice, while others limit customization or include hidden costs in swaps. For example, Coin Wallet has a minimum service fee to support wallet development, server maintenance, and team operations.
Here’s a breakdown of how popular crypto wallets compare in terms of fees and functionality. Keep in mind that these metrics can change, so you should always verify the latest information.
All information about Coin Wallet fees you can check here.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are Ethereum gas fees so high?
Ethereum gas fees are high because they reflect real-time demand for block space. When many users are sending transactions or interacting with smart contracts — such as during NFT launches or market volatility — the network becomes congested. As a result, users must bid higher fees to prioritize their transactions. Fees are also influenced by smart contract complexity and transaction type.
Can I avoid crypto transaction fees completely?
You can’t avoid blockchain transaction fees entirely, but you can minimize them significantly. Using low-fee networks (like Solana or Polygon), Layer 2 solutions (such as Arbitrum or zkSync), or batching transactions can help reduce costs. Some centralized platforms may offer “fee-free” transfers within their ecosystem, but those usually come with other trade-offs like custodial control.
Which crypto wallet has the lowest fees?
Wallets like Coin Wallet, MetaMask, and Trust Wallet don’t charge extra fees for basic crypto transfers — they only pass along the network fee. However, the ability to choose cheaper networks, use Layer 2, or adjust gas settings plays a bigger role in reducing costs. Wallets with built-in exchanges (like Atomic or Exodus) may add a spread or service fee on swaps.
How do I track gas fees in real time?
You can monitor live gas prices using crypto gas tracker tools like Blocknative Gas Estimator, ETH Gas Station, Etherscan Gas Tracker. These platforms show current fees for slow, average, and fast transactions, along with estimated confirmation times. Tracking gas helps you choose the best moment to send and reduce Ethereum gas fees.